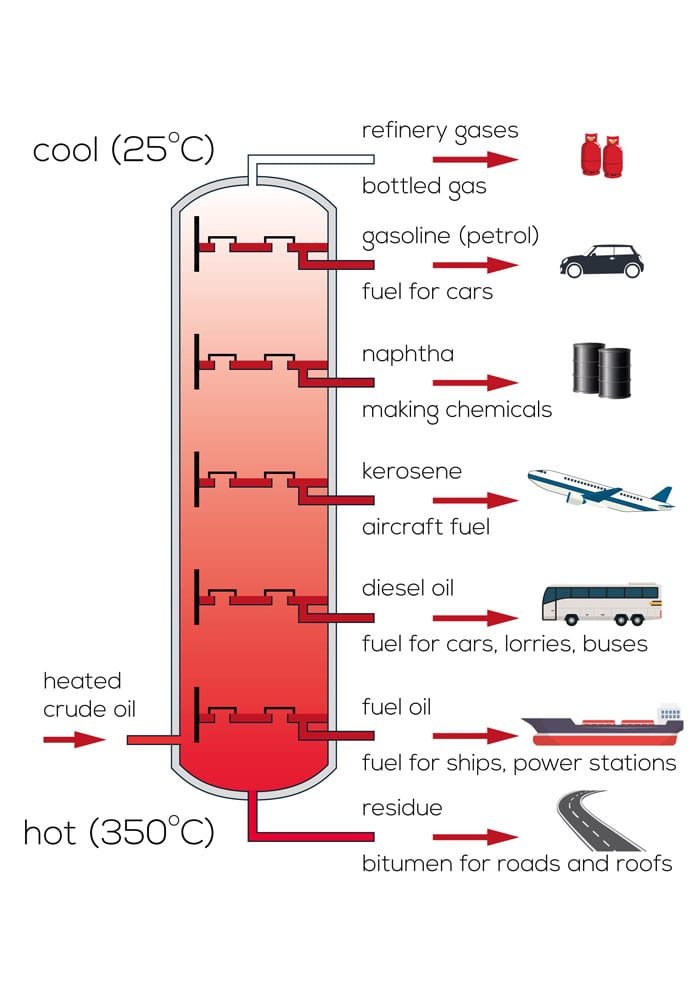
LPG is an environmentally friendly source of energy with a wide range of applications: domestic (heating, cooking, hot water production), industrial, agricultural, catering and automotive fuel. LPG is used in hundreds of applications by millions of users throughout the world. When LPG is burnt, it produces the cleanest emissions of all oil-based products, with a low carbon dioxide output.
LPG stands for “Liquefied Petroleum Gas”. The term is widely used to describe two prominent members of a family of light hydrocarbons called “Natural Gas Liquids” (NGLs): propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10). The other two members of the NGLs family, ethane and condensates, have their own distinctive markets.